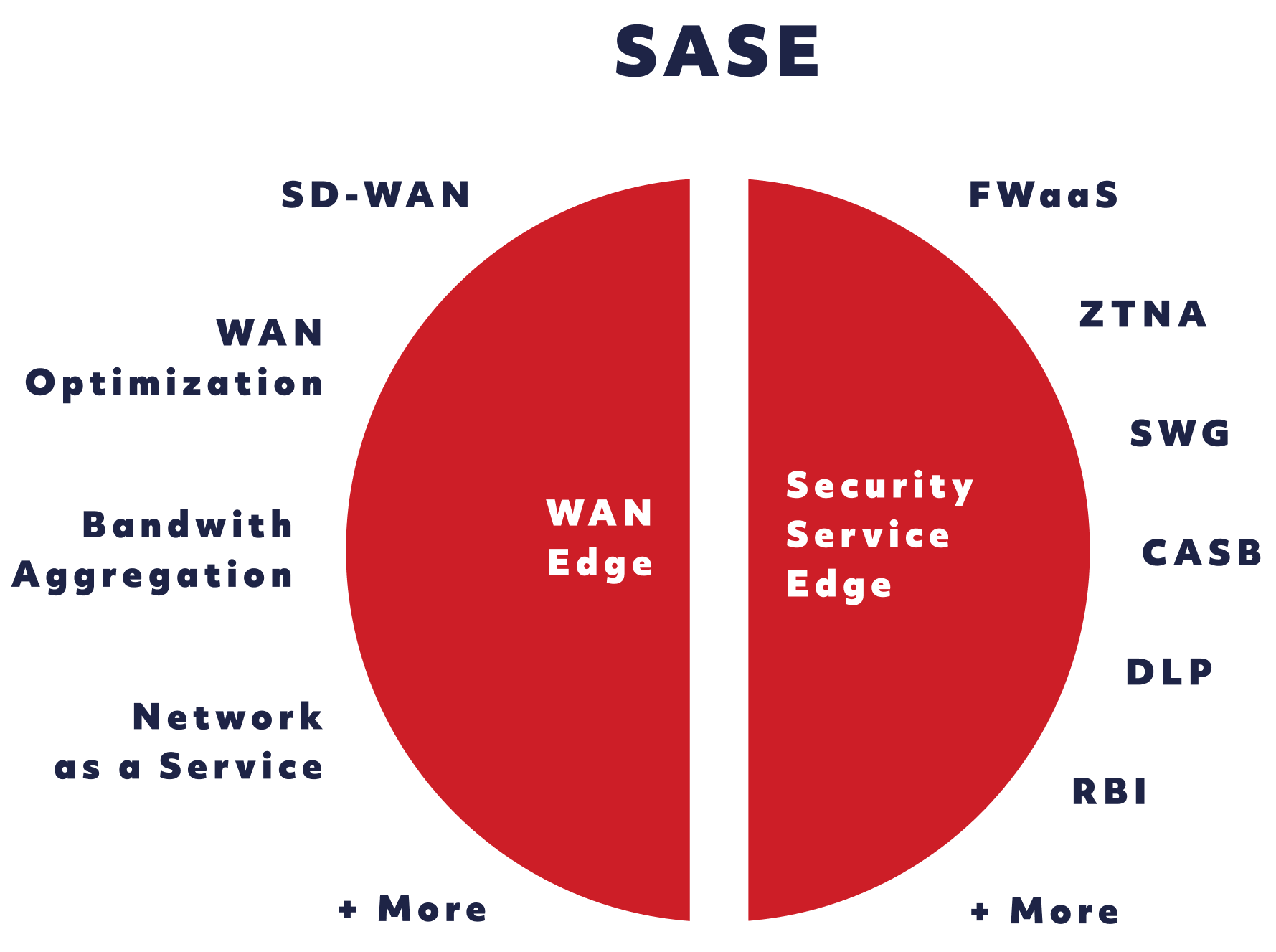
Introduced by Gartner in 2019, SASE - Secure Access Service Edge is defined as a global cloud-based service that delivers converged network and security-as-a-service capabilities for all edges. SASE is primarily delivered as a service and enables zero trust access based on the identity of the device or entity, combined with real-time context and security and compliance policies.
The primary components of a SASE Architecture include:
- Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN): SASE leverages the capabilities of SD-WAN to provide optimized network routing between SASE points of presence (PoPs).
- Firewall as a Service (FWaaS): A firewall is the foundation of any network security stack. SASE includes FWaaS to provide strong protection with minimal overhead and management.
- Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA): ZTNA (also called SDP) offers an alternative to legacy secure remote access solutions that embraces zero-trust policies and provides access to resources on a case-by-case basis.
- Secure Web Gateway (SWG): SWG solutions protect users against malware, phishing, and other Internet-borne threats. SASE offers SWG protection to all users, regardless of their location.
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB): A cloud-based security solution like SASE logically needs to provide security for cloud applications. CASB is integrated into SASE to monitor and secure access to cloud-based resources.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): SASE leverages DLP to help protect against data loss and potential breaches by controlling the movement of data in and out of cloud applications.
- Consolidated Management: Complex and disconnected security is one of the main challenges that SASE is designed to solve. SASE users should be able to monitor and manage all their security solutions from a single pane of glass.